When you’re designing or sourcing a plastic component, one of the biggest challenges is selecting the right material. With hundreds of plastics available, each with its own performance profile, the choice can feel overwhelming. That’s where the Plastics Pyramid comes in — a simple but powerful guide that categorizes plastics by performance, structure, and suitability for different applications.
At SRT Plastics, we work with both engineering teams and purchasers to ensure that every project starts with the right material foundation. Below, we’ll walk you through the pyramid and what it means for your applications.
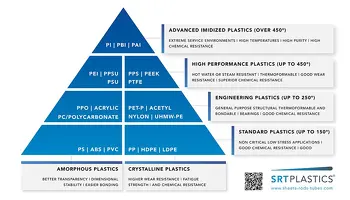
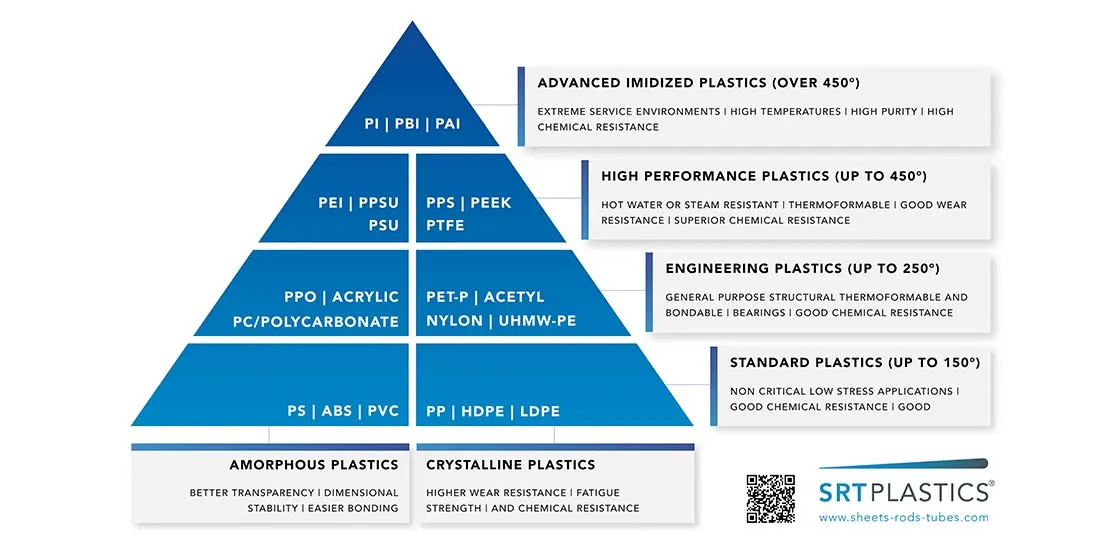
Four Levels of Performance
The pyramid is structured in layers, starting from commodity materials at the base and rising to advanced, high-performance plastics at the top:
Commodity & Standard Plastics
These are the everyday workhorses of the plastics world — cost-effective, easy to process, and widely available. Materials like PVC, ABS, PP, and HDPE are common here. They’re ideal for non-critical, low-stress applications where affordability and ease of fabrication matter.
Engineering Plastics
Moving up the pyramid, materials like Polycarbonate (PC), Nylon (PA), and Acetal (POM) offer a step change in strength, wear resistance, and durability. These are used when components must perform structurally or withstand moderate heat and chemical exposure.
High-Performance Plastics
At this level, we find PEEK, PEI, PPSU, and PTFE — materials known for their ability to resist high temperatures, harsh chemicals, and demanding mechanical loads. They’re often specified in industries with strict compliance standards, such as food, healthcare, and cleanroom environments.
Advanced Imidized Plastics
At the very top sit materials like PBI, PI, and PAI. These deliver extreme temperature resistance, chemical stability, and wear performance. They are more difficult to produce and are often reserved for aerospace, defense, and other mission-critical applications.
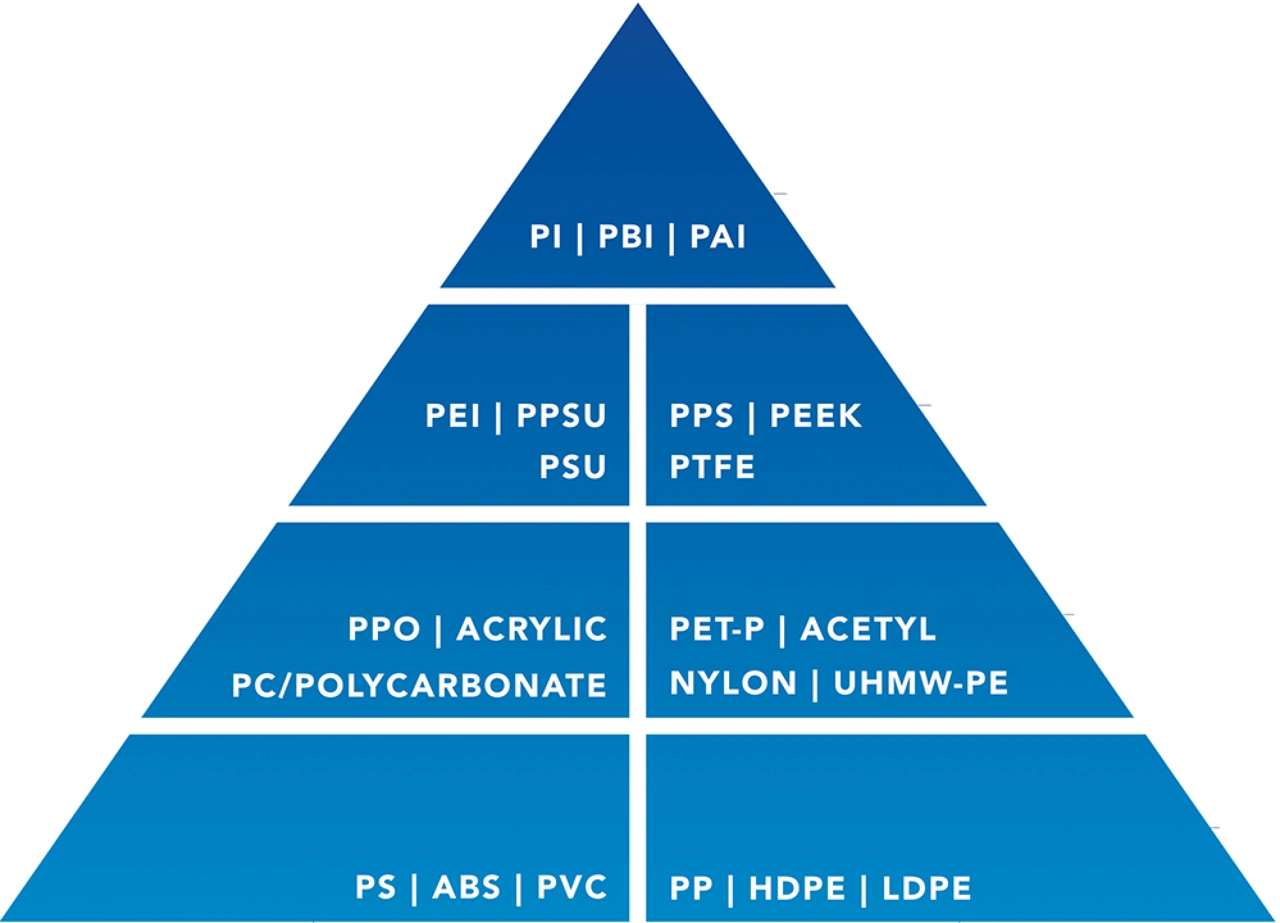
Amorphous vs. Crystalline
The pyramid also divides plastics into two structural families:
- Amorphous plastics (e.g. PC, ABS, PVC) — better transparency, dimensional stability, and easier bonding.
- Crystalline plastics (e.g. PP, POM, Nylon) — higher wear resistance, fatigue strength, and chemical resistance.
Understanding this distinction helps us match not just the performance level but also the processing and application behavior of each plastic.
Why This Matters
Choosing the wrong plastic can mean premature wear, chemical attack, or even catastrophic failure. Choosing the right one means reliability, compliance, and cost-effectiveness. At SRT Plastics, we don’t just fabricate parts — we help you navigate the plastics pyramid to ensure your material is the right fit for your design, your environment, and your budget.
Work with a Partner Who Knows Plastics
Whether you need a simple cover from a commodity material, a structural panel in an engineering plastic, or a high-performance cleanroom component, SRT Plastics is here to advise and deliver.
Contact us to discuss your next project and let’s select the right material together.